
Author Affiliations
Abstract
National Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on Tunable Laser, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
The phase-sensitive optical time-domain reflectometry (φ-OTDR) is a good candidate for distributed dynamic strain sensing, due to its high sensitivity and fast measurement, which has already been widely used in intrusion monitoring, geophysical exploration, etc. For the frequency scanning based φ-OTDR, the phase change manifests itself as a shift of the intensity distribution. The correlation between the reference and measured spectra is employed for relative strain demodulation, which has imposed the continuous measurement for the absolute strain demodulation. Fortunately, the Brillouin optical time domain analysis (BOTDA) allows for the absolute strain demodulation with only one measurement. In this work, the combination of the φ-OTDR and BOTDA has been proposed and demonstrated by using the same set of frequency-scanning optical pulses, and the frequency-agile technique is also introduced for fast measurements. A 9.9 Hz vibration with a strain range of 500 nε has been measured under two different absolute strains (296.7με and 554.8 με) by integrating the Rayleigh and Brillouin information. The sub-micro strain vibration is demonstrated by the φ-OTDR signal with a high sensitivity of 6.8 nε, while the absolute strain is measured by the BOTDA signal with an accuracy of 5.4 με. The proposed sensor allows for dynamic absolute strain measurements with a high sensitivity, thus opening a door for new possibilities which are yet to be explored.
fiber optics sensor Rayleigh scattering Brillouin scattering fast measurement Opto-Electronic Advances
2020, 3(12): 12200013

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on Tunable Laser, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
2 The 29th Research Institute of China Electronics Technology Group Corporation, Chengdu 610036, China
Optical chirp chain Brillouin optical time-domain analysis (OCC-BOTDA) has the capabilities of fast measurement, high Brillouin threshold, and freedom from the nonlocal effect; at the same time, however, it also has problems introduced by transient stimulated Brillouin scattering. The influence of the transient interaction is reflected as the broadened asymmetric Brillouin spectrum, the ghost peak, and the frequency shift of the main peak. This introduces difficulty in computing the fiber Brillouin frequency shift with good measurement accuracy. Besides, the OCC modulation causes additional noise due to the uneven amplitude response for different frequency components. In this work, we propose a high-performance OCC-BOTDA using the principal component analysis (PCA) based pattern recognition algorithm and differential pulse-width pair (DPP) technique. After building the Brillouin spectrum database (i.e., all patterns), the fiber intrinsic Brillouin frequency shift can be recognized by the PCA algorithm from a nonstandard Brillouin spectrum profile, resulting in good measurement accuracy. Meanwhile, the DPP technique, subtracting between two Brillouin signals generated by two wide-width pump pulses, is utilized to reduce the OCC modulation noise and avoid the pulse self-phase modulation effect in long-range BOTDA sensing. In the experiment, a temperature measurement with 1.3?MHz measurement precision, 4?m spatial resolution, and 5?s measurement time is achieved over a 100?km single-mode fiber.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(6): 06000652
哈尔滨工业大学可调谐激光技术国家级重点实验室,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150001
布里渊光纤传感通过光纤中受激布里渊散射效应实现温度和应变测量,具有空间分辨率高、传感距离长和测量精度高等特点,因此分布式布里渊光纤传感成为近年的研究热点。本文通过对长距离分布式布里渊光纤传感研究进展的调研和分析,概括了长距离布里渊传感面临的主要限制因素和解决的关键技术,重点介绍了基于时分复用、频分复用、脉冲编码、宽带频率调制和图像处理算法的长距离布里渊光纤传感技术。随着长距离布里渊光纤传感器的实际工程化,对于快速测量的需求愈发显著,这将是未来长距离布里渊光纤传感的主要研究方向。
受激布里渊散射 布里渊光时域分析 光纤传感 非线性光学 stimulated Brillouin scattering Brillouin optical time domain analysis optical fiber sensing nonlinear optics
1 哈尔滨工业大学可调谐激光技术国家重点实验室, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150001
2 哈尔滨工业大学土木工程学院, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150001
近些年,分布式布里渊光纤传感因具有分布式应变和温度的测量能力, 以及在结构健康监测领域的重要应用而受到广泛的研究。在多种传感方案中, 布里渊光时域分析(BOTDA)技术具有信噪比好、空间分辨率高、传感距离远等优点, 受到广泛关注。传统的BOTDA系统平均和扫频过程比较费时, 只适宜进行静态或缓慢的应变测量。通过分析BOTDA系统的分布式传感原理, 总结了限制其快速分布式传感测量的主要因素。针对这些限制因素, 综述了近期快速BOTDA系统取得的一系列的进展, 主要包括基于偏振补偿技术的快速BOTDA系统、基于光学捷变频技术的快速BOTDA系统、基于斜坡法的快速BOTDA系统、基于光学啁啾链的快速BOTDA系统、基于光学频率梳技术的快速BOTDA系统, 指出通过单一或者多个新技术组合而成的快速BOTDA系统具有更好的性能和更广阔的应用前景。
传感器 非线性光纤光学 受激布里渊散射 振动分析
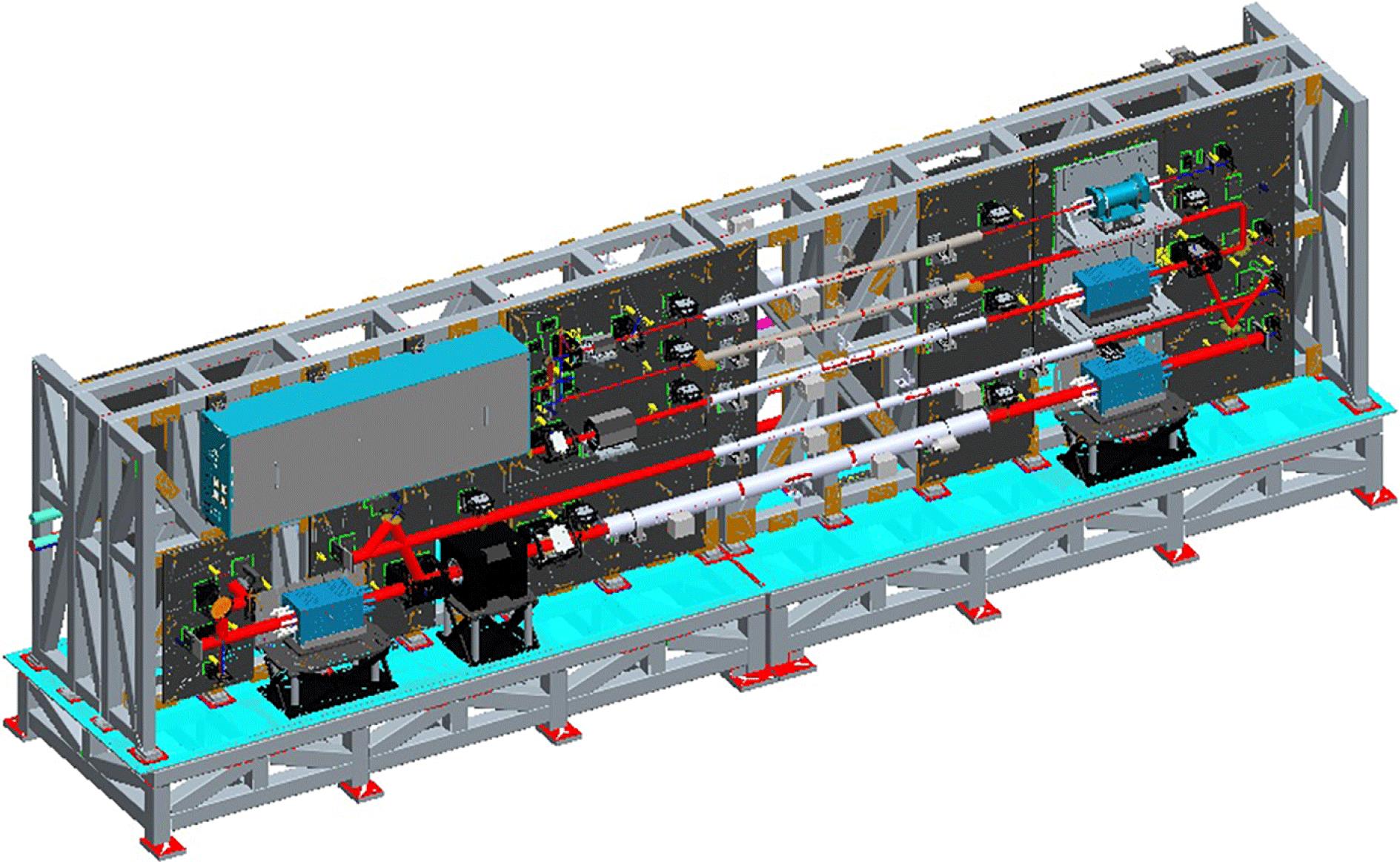
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on Tunable Laser, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
2 Research Center of Laser Fusion, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621900, China
A 100-J-level Nd:glass laser system in nanosecond-scale pulse width has been constructed to perform as a standard source of high-fluence-laser science experiments. The laser system, operating with typical pulse durations of 3–5 ns and beam diameter 60 mm, employs a sequence of successive rod amplifiers to achieve 100-J-level energy at 1053 nm at 3 ns. The frequency conversion can provide energy of 50-J level at 351 nm. In addition to the high stability of the energy output, the most valuable of the laser system is the high spatiotemporal beam quality of the output, which contains the uniform square pulse waveform, the uniform flat-top spatial fluence distribution and the uniform flat-top wavefront.
design design frequency conversion frequency conversion laser amplifiers laser amplifiers laser engineering laser engineering laser systems laser systems light propagation light propagation modeling modeling nonlinear optics nonlinear optics optimization optimization wavefront correction wavefront correction High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2016, 4(1): 01000e10





